
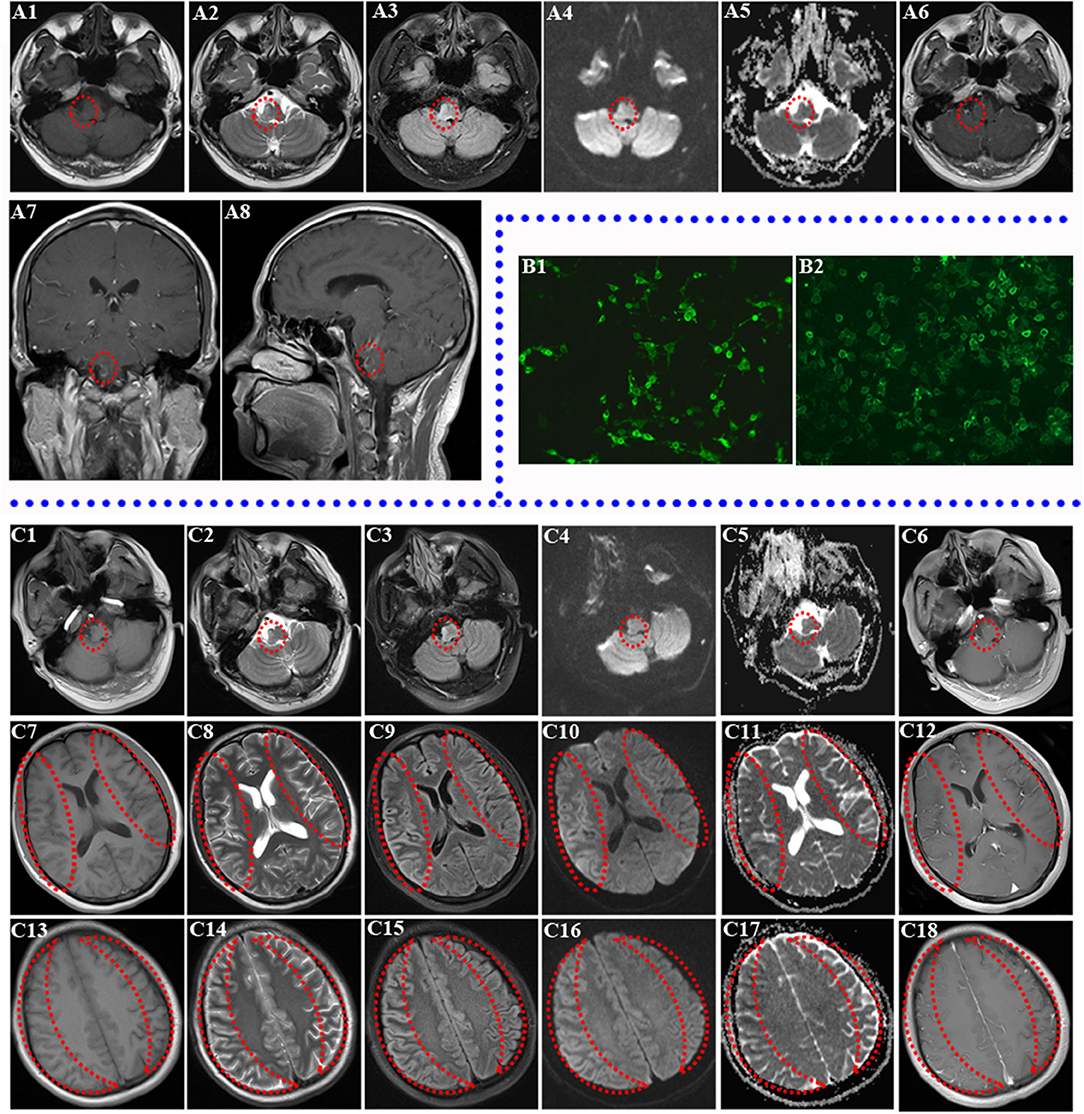
Furthermore, several experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE) models induced by MOG protein appear to mimic the NMO phenotype, especially in Brown Norway rats ( Collongues et al., 2012). However, passive transfer of purified human AQP4 antibodies alone without blood–brain barrier breakdown is not sufficient to induce NMO in animal models ( Jones et al., 2012). The main pathogenic characteristic of NMO is the presence of AQP4 antibodies in the serum and/or CSF this has been shown in patients and also in animal models. From that point forward, NMO was considered a separate entity. However, in 2004 a specific antibody-known initially as anti-NMO-IgG, and then later as AQP4 antibody-was found to distinguish NMO from multiple sclerosis ( Lennon et al., 2004). Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) was long considered to be a subtype of multiple sclerosis. In this issue of Brain, Jurynczyk and co-workers describe the largest cohort of patients to date with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody (MOG-antibody) neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) and confirm two important points: (i) the clinical expression of MOG antibody may be included in the broadest definition of NMOSD and (ii) the clinical profile of MOG-antibody-positive patients differs from that of patients with aquaporin-4 (AQP4)-antibody NMOSD ( Juryńczyk et al., 2017 a).
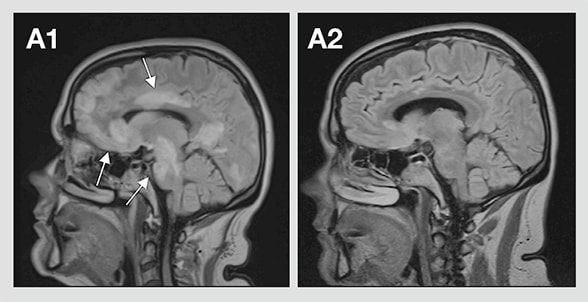
This scientific commentary refers to ‘Clinical presentation and prognosis in MOG-antibody disease: a UK study’, by Jurynczyk et al.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
